Practical 3-3:
Set Web Browser Security
This practical requires Windows Internet Explorer (IE) Version 7 Web browser and above to do.
Through this, I will learn how to do various security settings on the browser which can help protect my computer from the different threats out there on the net.
The security settings I would be doing are the cookies, Add-ons, Security Zones, Restricted Zones, privacy level and pop-up blocker.
Cookies
Tools > Internet Options > General Tab > Browsing History > Settings > View files
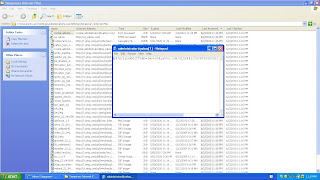
(Figure 3.2.1)
It has different kinds of information like where the user frequently browse which hackers can make use of to upload viruses on these websites without the knowledge of the user who is surfing the website.
Add-onTools > Manage Add-ons
Add-ons are additional programs that are needed to run things like media applications and other applications on the web browser. Examples of these are Java and Javascript. These settings allow user whether to enable/disable the add-ons used on the web browser.
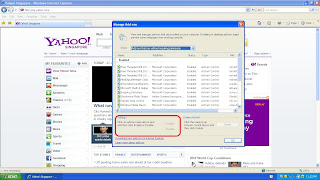
(Figure 3.3.2)
As shown in the red box in Figure 3.3.2, this is where users can enable/disable the add-ons.
Security ZonesTools > Internet Options > Security tab
Moving the slider of the Security level for this zone allows various settings.
Medium - prompts before downloading potential unsafe content and unsigned ActiveX controls.
Medium-high - Appropriate for most websites, prompts before downloading potential unsafe content and unsigned ActiveX controls.
High - Appropriate for websites that might have harmful content, maximum safeguards and less secure features are disabled.
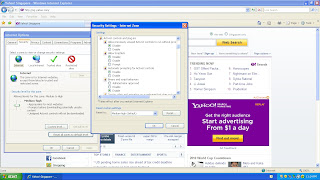
Figure 3.3.3
This is where user would do their own custom settings for security zones.
Restricted Zones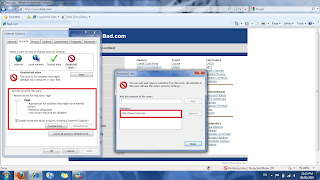
Figure 3.3.4
When a website is added to the restricted zones, the next time the user enters that website, the security levels would automatically change to the High security level so that it is able to prevent malicious activity from happening.
Privacy LevelTools > Internet Options > Privacy
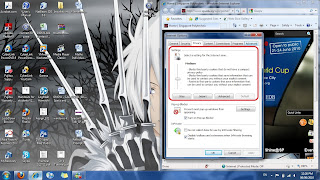
Figure 3.3.5
It helps block cookies from being seen by other websites who try to use this to know peoples' browsing habits.
Pop-up blockerTools > Pop-up blocker > pop-up blocker settings
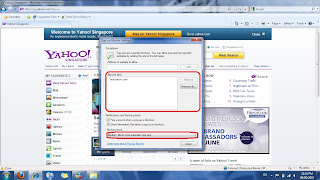
Figure 3.3.6
As what is name suggest, it is used to block unwanted pop-ups that the user does not want to receive. User can adjust the settings to set whether they want all the pop-ups to be block.